E-commerce Website Redesign
Enterprise Technical SEO

Overdrive Interactive generated this image in part with OpenAI’s DALL·E on 2022-10-05
There are several important technical SEO practices to implement to ensure your website is indexed and you are employing a strong enterprise SEO strategy. Your digital marketing agency should be performing a Critical Issues Assessment to check and monitor these factors. Included in the assessment (to start), an enterprise eCommerce SEO team should be checking the use of a Robots.txt file, XML sitemaps, language country tags, faceted navigation, and canonicalization. In this article, we’ll discuss these and other important enterprise SEO services and practices so that you’ll be better equipped to use these tactics to make sure that your website is found by more users.
SEO teams use a combination of SEO platforms for eCommerce websites and large-scale projects as part of an enterprise SEO website audit, to identify technical issues and opportunities for SEO campaign development. Common enterprise SEO tools include site crawlers like Screaming Frog, as well as ranking tools such as Brightedge.
Becoming a Marketing Engineer – Webinar Slides & Video
Learn how all the best practices and platforms we use come together to create a marketing infrastructure, customer journey, and sales funnel.
Watch the Webinar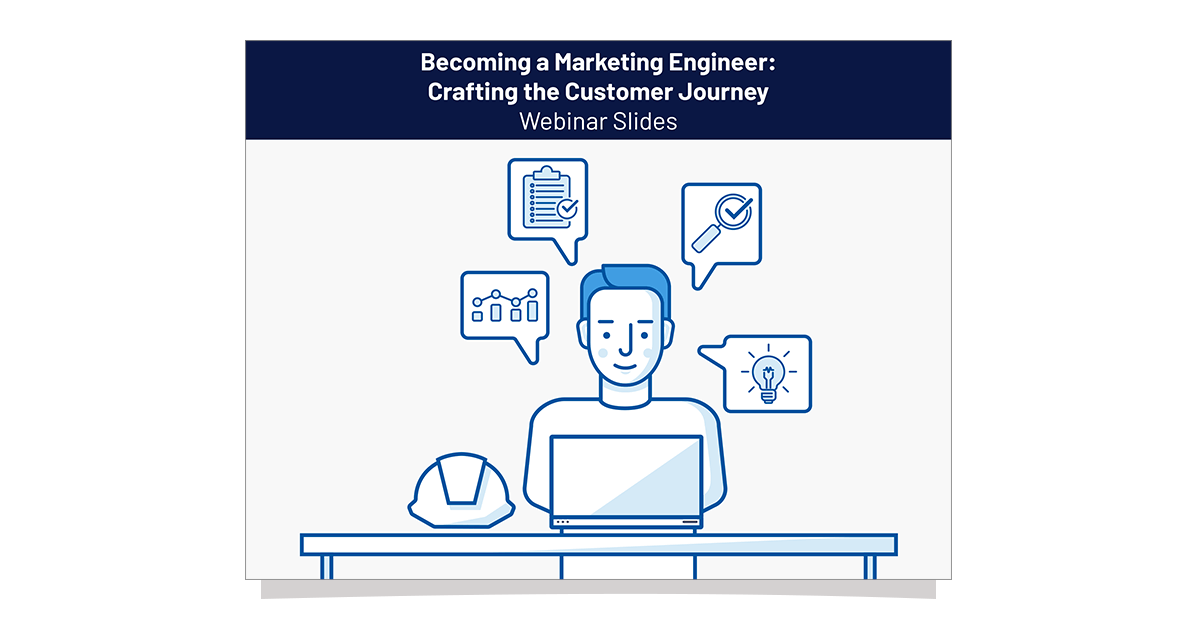
What is enterprise technical SEO?
Enterprise technical SEO refers to optimizations made to an enterprise website that help search engine crawlers crawl and index an enterprise website and ultimately improve organic rankings. Enterprise technical SEO is not much different from technical SEO done on any other site, it just scales differently and usually involves more teams to partner with to have optimizations implemented.
Here are a few of the most important enterprise technical SEO elements you should have on your site for improved organic search and traffic:
robots.txt file
One of the most overlooked elements of technical SEO is the robots.txt file. This file controls the behavior of bots and crawlers that visit a website. When it is not used properly, bots and crawlers may ignore portions of the file and potentially open attacks on your site. A few things to consider when using the robots.txt file:
- What sections of your site should a crawler not go to? If you have pages or whole sections of your site that a crawler should not navigate to, look to implement disallow commands.
- What bots should be crawling your site? The robots.txt file allows you to target specific robots or spiders by phrase to keep them from crawling or have specific rules for their crawls.
- Is your sitemap listed within your robots.txt file? It is best practice to provide reference to your website’s sitemap so crawlers can easily find it and the pages you want to be crawled.
- Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
The X-Robots-Tag HTTP header controls the appearance of non-HTML content in search results. Blocking Google from crawling your pages will result in your pages not showing up in search results. However, it is possible to use a meta robots tag to specify which elements you want to be crawled. The X-Robots-Tag is an excellent way to block specific elements.
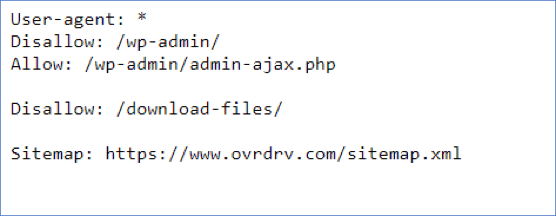
XML sitemap
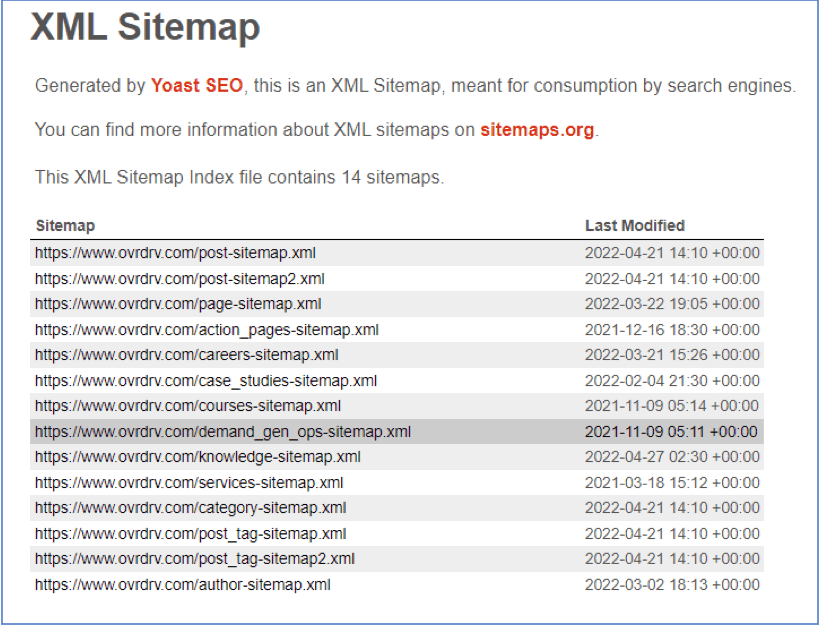
Using an XML sitemap is an integral part of enterprise technical SEO. Search engines are more likely to see new content in SERPs when it is included in the sitemap. Leaving out several pages from the sitemap will result in a decrease in organic traffic and rankings due to pages potentially not being seen or crawled as search engines may ignore new content, which will result in lower rankings and traffic. Hence, it is important to include only canonical pages in the XML sitemap that you wish to be considered for ranking and indexing. Some things to consider with XML Sitemaps:
- Break your sitemaps into location, video, news, and image-specific sitemaps to segment your content and asset types as part of your enterprise SEO strategy.
- XML Sitemaps are not a substitute for normal web crawling so consider implementing a strong internal linking process across your website so that you have good site navigation.
- Consider creating an HTML version of your sitemap that is linked in the footer of your website. HTML sitemaps can be helpful to search engines and users to understand the structure of your site.
Site navigation

One of the most important elements in enterprise technical SEO of any website is site navigation. Good site navigation will improve the user experience, reduce bounce rates, and make your site easier to crawl; site navigation is not just important for users, but also for search engines.
User experience
Search bots use sitemaps and links to understand the structure of your site and which pages are most important to your site and which ones aren’t. Though many website optimization tips emphasize the importance of crawlability, it’s important to focus on the user experience and avoid compromising on the ease of use.
Enterprise website navigation should help visitors quickly find the information they need. Make sure the most important pages are linked as “tier 1” items in your navigation; the number of such pages should be limited to seven. Don’t link “tier 4” pages to your navigation, because they may not be useful to your visitors.
Breadcrumbs
Another key element with site navigation is breadcrumbs. These are rows of internal links that allow visitors to quickly return to the previous section or root page. Some things to consider with breadcrumbs:
- Many breadcrumbs list the most general page as the first link, with more specific sections listed on the right. Consider your website’s structure and flow for how breadcrumbs should be set up.
- Make sure to use breadcrumb structured data markup for these links. This allows easier consumption and understanding of your site by crawlers.
- Breadcrumb links should be positioned in the header of your website, not on the side.
Whether you’re a fashion retailer, digital publisher, or restaurant, you should consider how your site’s navigation affects search engine rankings. Once you’ve determined the best site navigation strategy, you can make a lot of changes in a single place.
Internal linking structures
Developing a strong internal linking strategy will help your enterprise website to be found by search engines. It’s a process that starts with assessing your main pages and identifying opportunities for interlinking. Incorporating keywords that describe your products and services into the anchor text of internal links will help you build an effective link structure that will increase your web traffic and revenue.
For example, if you’re an e-commerce website, it’s important to use specific keywords when writing the anchor text for your internal links.
Next, identify the various hub pages that cover the different topics and search intent. These pages will form a topic cluster. Having a pillar page that covers a particular topic and many supporting cluster pages will help search engines understand what your website is all about. Then, to generate more traffic, you can start setting up more internal links.
Creating internal links is crucial because it helps your website build a hierarchy. Internal links also pass link juice from important pages to less important ones. Strong internal linking structures are an effective way to continuously improve your ranking.
Canonicalization
While it isn’t as straightforward as making a single page the primary copy, canonicalization is an important part of enterprise technical SEO. Enterprise-level design of a website should consider planned content creation and content marketing with an eye towards international SEO for best practices on canonicalization.
Canonicalization is the process of adding the same content to several URLs. It eliminates duplicate content and prevents search engines from selecting the wrong one as the “original” version. The process involves including the canonical tag in the HTML code.
For example, if Page A has similar content to Page B, adding the same content to both pages can improve SEO performance.
If canonicalization is not implemented, web crawlers will index multiple versions of a page (especially important for faceted navigation and eCommerce websites ex: shoes, blue suede vs blue suede shoes) and water down the SEO potential.
It’s critical to implement canonical tags correctly. Google may sometimes choose a different canonical for certain pages, but this won’t affect ranking.
John Mueller of Google recommends that webmasters review these signals for confusion, as the links from the canonical page to the canonicalized page may confuse Google’s indexing process, and it will combine these signals to make a final decision based on what’s best for your site.
Language and country tags
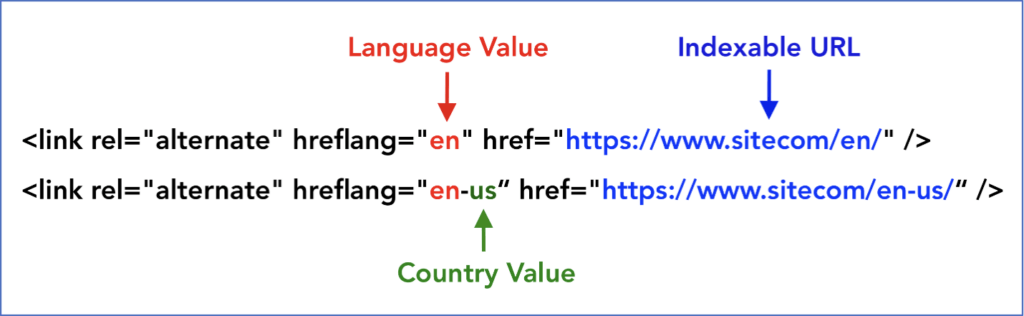
Using hreflang tags is extremely important for your website. This tag allows search engines to automatically determine the country and language of a website. When a user clicks on your website, the hreflang value directs them to the preferred version of your website.
Make sure that your website uses both language and country tags as part of your enterprise international SEO strategy. Language and country tags (also referred to as rel=”alternate” hreflang=”xx-xx”) are communicated to Google through the hreflang and canonical tags, which should be used in conjunction for multiple language enterprise sites.
Your enterprise SEO agency should review to ensure these tags are used to specify the versions of your site in different countries and languages. It is important to note that this can get complicated if you have many variations of the same languages across your website.
It is a good idea to have a full set of tags for each page, which should be placed as a link attribute on a web page. In addition, you should use the HTTP protocol header to communicate your website’s language variations.
Schema code
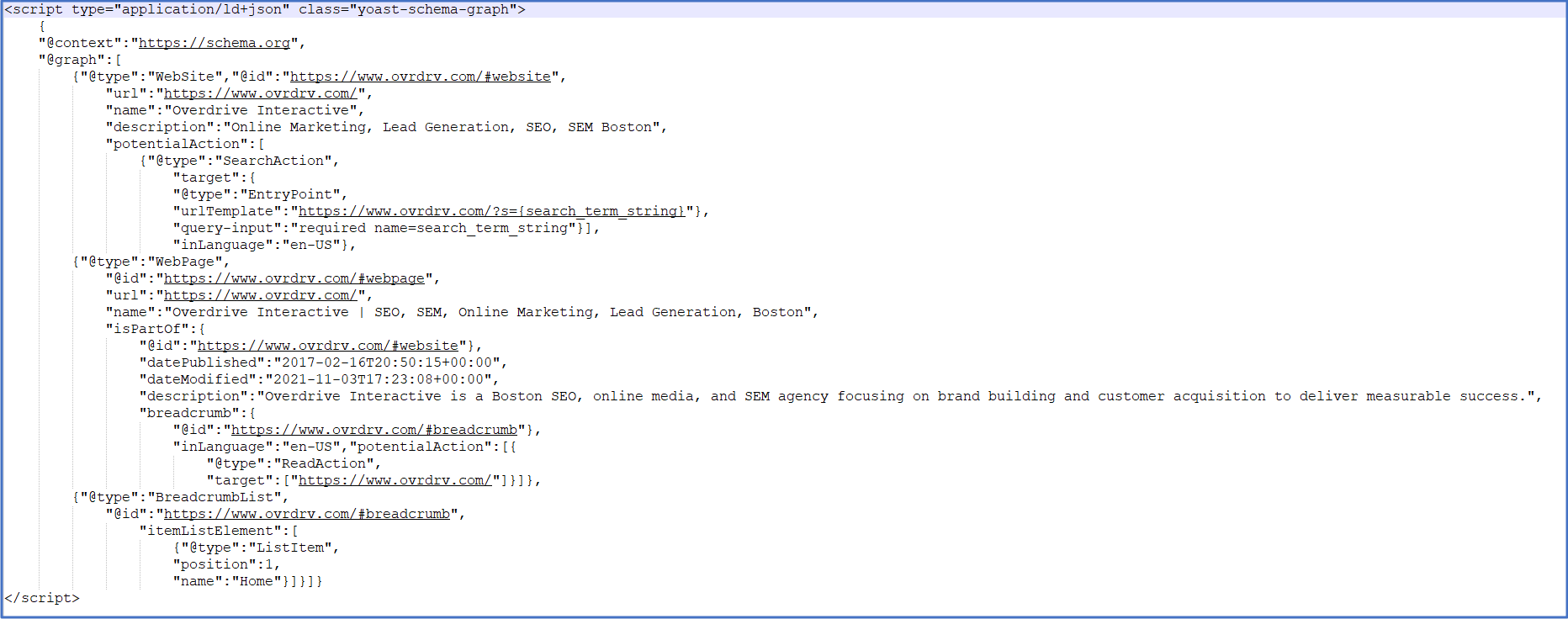
Schema markup is a standardized way to tell search engines what data means on your website and help your enterprise achieve its SEO goals. It was created by industry experts with your users in mind and has significant SEO benefits. By adding this code to your website, you can improve your brand’s visibility, increase click-through rates, and make your pages more engaging. There are many other benefits to using schema markup on your website. Here are a few of them:
- Ability to rank in rich snippets. Schema code helps enterprise organizations get displayed in additional search results page features, adding more opportunities for your website to be seen by users.
- Provide business-level information to Google for them to better understand your business entity and what your business does and/or is about.
- Provide product level information to help rank within google shopping.
- Provide online reviews of your business that are curated by your enterprise and show how you help your customers.
When integrating schema, be sure to include all the necessary information for the schema type that you are using. Including all of the fields that are mandatory, as well as recommended ones that can help your users get the most relevant results. For example, you may choose to include your physical location.
Ensure the markup is error and warning-free by using the Schema Markup Validator and Google’s Rich Results Test.
The more properties your business has, the better. The more detailed information you provide on your website, the more likely it is that search engines will rank it higher in the SERPs for local queries across your many locations.
301 redirects
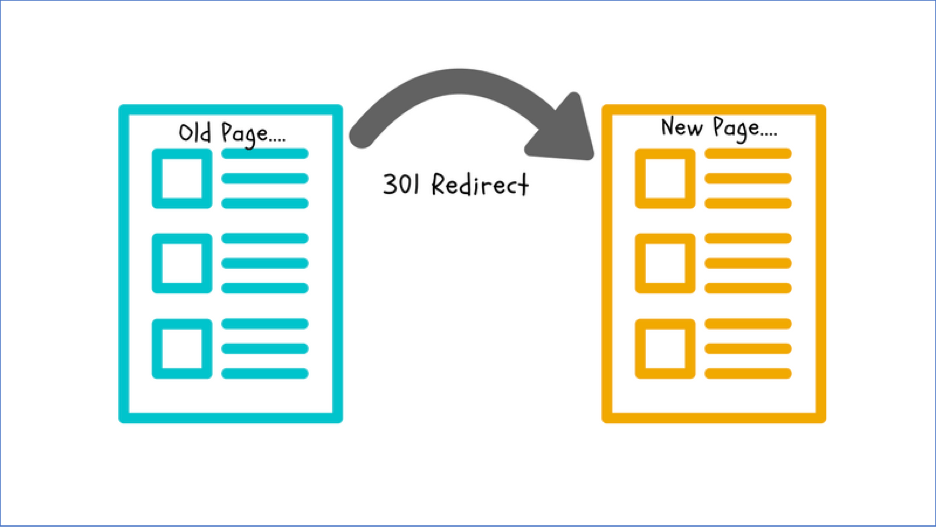
There are many reasons why an web page might change URLs, including discontinued products, domain or subdomain name changes, or a website redesign. Enterprise SEO website migrations and consolidations require special attention, particularly regarding 301 redirects.
301 redirects are an essential SEO tool. They let search engines know that a web page has moved or been deleted and that the new page should inherit the authority of the old one. Google will replace the original URL with the new one while assigning link equity to the new URL.
When used correctly, a 301 redirect will maintain the flow of traffic, rankings, and links as the user makes their way through a website’s architecture. This transition is smooth and seamless for the visitor.
Another benefit of 301 redirects is the ability to merge the traffic from a website’s original posts with traffic from a new page. Previously, webmasters would need to contact backlink providers for each post to get an effective backlink. They can avoid a backlink-building nightmare by implementing a proper 301 redirect so that backlinks point to new pages without having to reach out to anyone.
Core Web Vitals
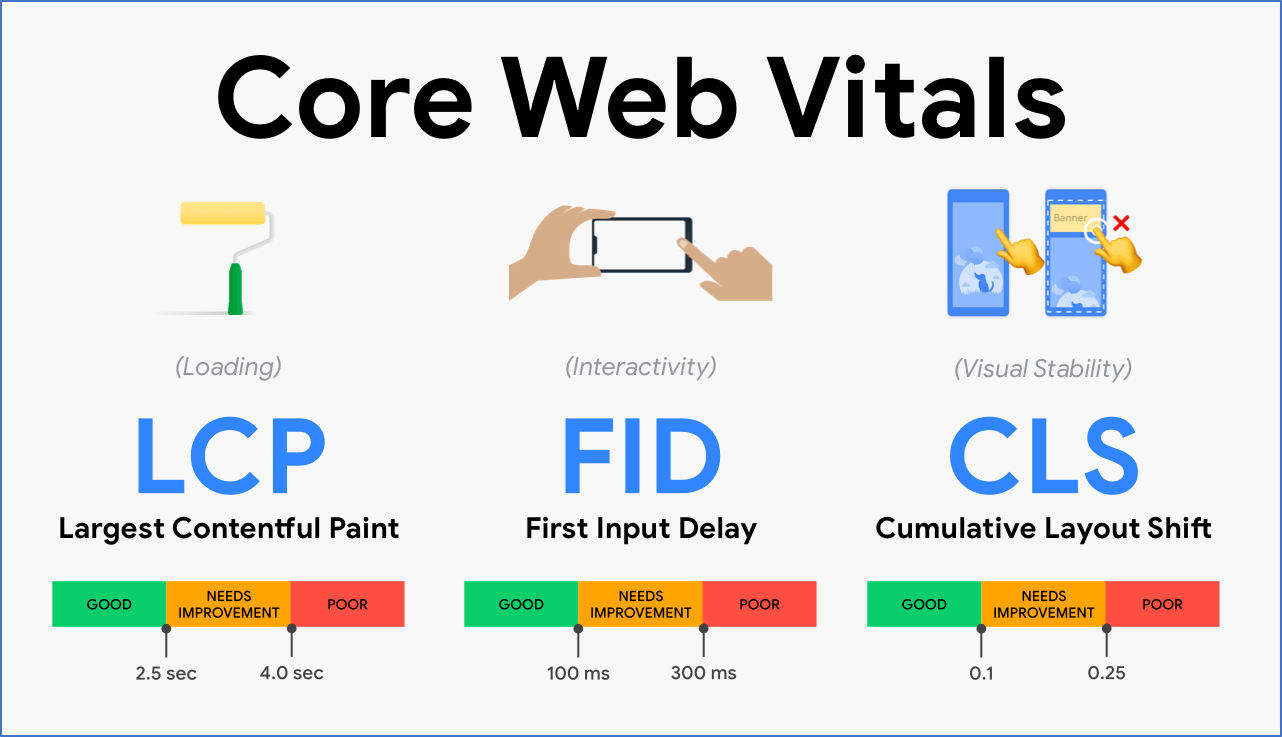
Core Web Vitals are metrics Google uses to gauge the user experience and functionality of a website. They measure three different factors:
- Load time
- Interactivity
- Visual stability of content as it loads
These three metrics help Google determine the ranking power of a page and if you are offering a good user experience. By positively implementing tactics around these measures, you can improve your site’s visibility in search results, improve conversions, and generate more leads and sales. However, they aren’t the only things you should consider.
The Core Web Vitals can be accessed through the GSC Insights tool under the “Experience” tab.
In addition, Google Lighthouse is a great option for performance testing. Lighthouse can help you identify elements that cause layout shifts in your website.
Page speed
One of the first steps to technical SEO success is ensuring healthy page speed. This is a very important part of the search engine optimization process, and if you are not making the most of your website’s speed, it could cost you valuable customers.
For one thing, slow pages and poor template design are a major inconvenience. It could increase bounce rates, reduce conversions, and even lead to a loss of revenue. Additionally, since page speed affects your rankings, if your pages take too long to load, they may not even show up in search results as Google may skip it altogether.
Fortunately, page speed optimization is possible even for enterprise companies, but it is often difficult to achieve such a high level of success.
Tips to Improve Page Speed
- Use CDN services or optimize your images
- Use a static page cache
- Re-test the page speed regularly
If your pages are slow, it will affect your visitors’ experience, causing a fall in ranking. You can take steps to improve page speed immediately, but first, you need to get regular, accurate insights. Run a web speed test using Google’s PageSpeed Insights.
SSL
Benefits of SSL Certificates
- SSL enables HTTPS, which improves your web presence and reputation with search engines.
- SSL enables you to protect your website from hackers and other threats.
- In addition to securing your website, it also protects your customer’s information and transactions.
- SSL certificates create a safer server-client connection. Once encrypted, data can’t be read by anyone except the intended recipient.
- A secure SSL certificate can help with PCI and DSS compliance requirements.
A secure website is a more trustworthy website. SSL helps Google reward websites that put the safety and security of their users first, and an SSL-enabled site is more likely to rank higher than a non-secure website. To make your website safe, install an SSL certificate on your website. This process can be costly, but it is worth the investment.
Installing an SSL Certificate
The process of installing an SSL certificate will depend on the type of certificate you choose and which provider you use. You can install an SSL certificate by yourself or hire a contractor.
You need to compile a URL map of all pages of your website. Once you’ve installed an SSL certificate on your website, it’s time to make the necessary updates to the site:
- Update your Google Search Console to reflect HTTPS.
- Update your XML sitemap to include HTTPS URLs only.
- Update social media links, email marketing software links, and social share counters to reflect HTTPS.
Qualys Lab can scan your SSL certificate installation and provide an overall grade.
Site structure
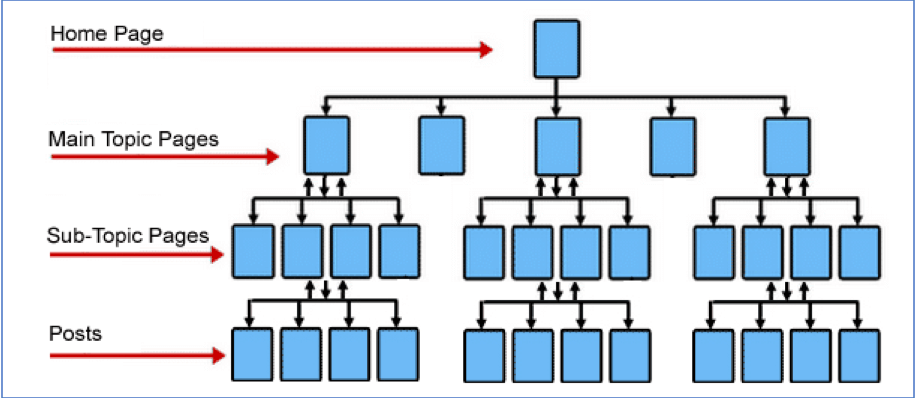
One of the best ways to optimize your enterprise website for search engines is to create a clear, logical site structure. You need to be aware of various website scenarios and consider how they might affect your site’s content, folder structure, URLs, schema, structured data, meta titles, and descriptions.
To achieve a great site structure, you must plan out your entire website so that the various components are in sync. The more relevant pages should be linked to the homepage, while the less-important ones should be further away from the homepage. This way, your website will be more easily crawled by search engines and will also be mobile-friendly.
Another aspect of enterprise technical SEO and your site structure is strategic keyword selection and associated preferred landing pages. Search engines can understand search terms better than humans and use algorithms called “Natural Language Processing” (Rank Brain, MUM, BERT) to decipher the intent of users. Therefore, companies should choose keywords related to the intent of the user.
Using commercial terms for content that is designed for the awareness stage is counterproductive to your SEO efforts. To keep users engaged, use terms that relate to your enterprise. The more relevant the terms, the more likely search engines will give your site a high ranking within the search results.
Website Indexing
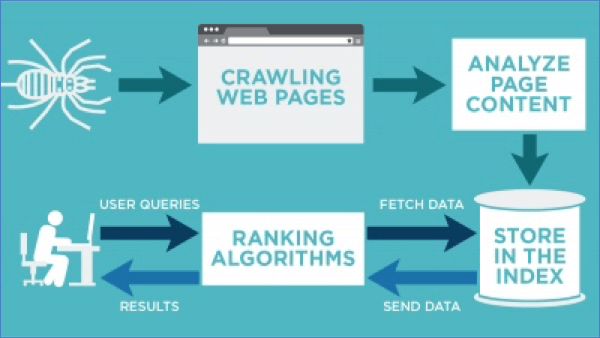
The first step in optimizing your website for the search engines is to ensure that it is properly seen and crawlable. Google will index your website when it finds optimal, relevant content that includes naturally relevant keywords and meta data (meta title and meta description).
The process of website indexing can take from a few hours to weeks, depending on the complexity of the site. Nonetheless, most pages are indexed within a few days or hours.
Website indexing is vital for enterprise SEO, but it’s not necessary to keep every page indexed. While many site owners want their content to be indexed, others don’t. For instance, a “thin” website with duplicate or overlapping content should not be indexed, as index bloat will reduce site search performance and eat up the crawl budget.
A healthy link profile is another essential part of any website indexing campaign. However, keep in mind that search engines prefer sites that load quickly, so making internal links too complicated, with too many backend codes, could result in slow page load.
Optimal content also means having a good balance of text and HTML code. If your site is confusing to indexers, it won’t be indexed at all. This is where technical SEO comes in.
Page Rendering
Page rendering affects the quality of search engine rankings, as search engines are able to read and understand the HTML. Thus, your website needs to have a good page rendering service. While rendering your website is not the same as coding it yourself, you can try using Google’s URL Inspector to examine how a page is rendered.
How Page Rendering Works
When a visitor views your website, they are greeted with two versions of the same HTML page:
- The initial HTML version of the page is rendered by the server.
- Server-side rendering is used to make the page faster, both for crawlers and users. This method requires a developer to implement it properly and is prone to slowing down the “Time to First Byte” (TTFB).
- The second HTML version is generated by the browser and is used by visitors to browse your site. This version is the one that passes the rendered page to the index.
Both versions are rendered using JavaScript frameworks.
The Drawbacks of JavaScript for Page Rendering
JavaScript-based web pages are incredibly slow to index, and developers are prone to overusing the technology to add glitzy functionality. This is detrimental to SEO, as it adds seconds to the page loading time.
Additionally, JavaScript rendering can also be harmful to UX and Core Web Vitals. By making the page load faster (try using Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool), you can improve the UX and core web vitals of your website.
So, before you use JavaScript, be sure to read the documentation on the optimization of JavaScript-based web pages.
Enterprise Technical SEO FAQs
What is included in enterprise technical SEO?
Technical SEO for enterprise websites includes the following elements, which affect search engine organic rankings and visibility:
- Crawling
- Website indexing
- Page rendering
- txt files
- XML sitemaps
- Site structure/architecture
- Faceted navigation
- Canonicalization
- Internal linking
- Broken links
- Schema and structured data markup
- Language and country tags
- 301 redirects and 404 HTTP errors
- Core Web Vitals
- Page speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- SSL certificates
- Security issues
Is technical SEO difficult for enterprise websites?
Technical SEO for enterprise websites can be challenging and difficult, as it involves many factors affecting a large number of webpages and the site as a whole. It can be complex, but is very important to manage as a website’s technical performance matters a great deal to search engines.
How do you conduct technical SEO for enterprise websites?
A technical SEO audit should be conducted for enterprise websites to ensure all elements are addressed. The audit should include (but is not limited to) analysis of the following:
- Full crawl of the website
- Crawlability and indexing issues
- Technical on-page elements
- Image issues
- Video and other media issues
- Internal linking
- External links
- robots.txt
- XML sitemaps
- Site speed and performance
- Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-friendliness
- Faceted navigation and canonicalization
- Schema and structured data markup
- SSL certificates and security issues
Scale Your SEO Program
Overdrive will provide the talent, technology, and process required to stand up, maintain, and optimize an always-on SEO program.